Table of Contents
- What is feline herpes eye infection?
- Signs and symptoms of feline herpes eye infection
- Causes of feline herpes eye infection
- How is feline herpes eye infection diagnosed?
- Treatment options for feline herpes eye infection
- Preventing the spread of feline herpes eye infection
- Managing recurrent feline herpes eye infections
- Home care tips for cats with herpes eye infection
- Complications of feline herpes eye infection
- When to see a vet for feline herpes eye infection
What is feline herpes eye infection?
How does the virus affect the cat’s eyes?
The virus primarily affects the cat’s upper respiratory tract, including the nasal passages, throat, and eyes. FHV-1 can cause inflammation of the conjunctiva, the thin, transparent membrane that covers the front of the eye and lines the inside of the eyelids.
What are the signs and symptoms of feline herpes eye infection?
The most common signs of feline herpes eye infection are squinting, redness, and discharge from the eyes. Affected cats may also experience watery eyes, inflammation of the eyelids, and sensitivity to light. In severe cases, ulcers or sores may develop on the surface of the eye, which can cause scarring and vision loss if left untreated.
How is feline herpes eye infection different from other eye infections?
Feline herpes eye infection is often confused with other eye infections, such as bacterial or fungal infections, due to the similar symptoms they produce. However, feline herpes eye infection is caused by a virus, and treatment usually involves antiviral medications instead of antibiotics.
In conclusion, feline herpes eye infection is a viral disease that affects cats’ eyes and can cause a range of symptoms, from mild irritation to severe inflammation and scarring. Understanding the signs and symptoms of this condition is crucial to seeking prompt veterinary care and preventing the spread of the virus to other cats.

Signs and symptoms of feline herpes eye infection
Feline herpes eye infection can produce a range of signs and symptoms that vary in severity from mild to severe. Some cats may only show mild symptoms that resolve on their own, while others may experience more severe symptoms that require veterinary treatment.
- Squinting
- Redness
- Discharge from the eyes
- Watery eyes
- Swollen eyelids
- Sensitivity to light
In some cases, affected cats may also experience sneezing, coughing, and nasal discharge.
How does feline herpes eye infection progress?
Feline herpes eye infection can progress rapidly, especially in cats with weakened immune systems. In severe cases, the infection can cause corneal ulcers, which are painful sores that form on the surface of the eye. If left untreated, these ulcers can lead to scarring and vision loss.
How long do the symptoms last?
The duration of symptoms can vary depending on the severity of the infection and the cat’s immune system. Mild cases of feline herpes eye infection may only last a few days, while more severe cases can last several weeks or longer. Some cats may experience recurrent episodes of infection throughout their lives.
Can feline herpes eye infection be mistaken for other eye conditions?
Feline herpes eye infection can be mistaken for other eye conditions, such as conjunctivitis or corneal ulcers. However, a veterinarian can perform diagnostic tests to confirm the presence of the virus and determine the appropriate treatment.
In conclusion, feline herpes eye infection can produce a range of signs and symptoms that can vary in severity and duration. Recognizing the signs of this condition and seeking prompt veterinary care is essential for preventing the infection from spreading and reducing the risk of complications.

Causes of feline herpes eye infection
Feline herpes eye infection is caused by the feline herpesvirus type 1 (FHV-1). This virus is highly contagious and can be transmitted from cat to cat through direct contact with an infected cat’s saliva, nasal secretions, or eye discharge.
How does the virus enter a cat’s body?
The virus can enter a cat’s body through the mouth, nose, or eyes. Once inside the body, the virus can travel to the respiratory tract and cause inflammation of the nasal passages, throat, and eyes.
How common is feline herpes eye infection?
Feline herpes eye infection is a common viral disease in cats, and most cats will be exposed to the virus at some point in their lives. However, not all cats that are exposed to the virus will develop symptoms of infection.
Which cats are at risk of infection?
Cats that are housed in crowded or stressful environments, such as shelters or multi-cat households, are at higher risk of infection. Additionally, cats that have weakened immune systems, such as kittens or older cats, are also more susceptible to infection.
Can feline herpes eye infection be prevented?
There is no foolproof way to prevent feline herpes eye infection. However, some steps can be taken to reduce the risk of infection, such as:
- Vaccinating cats against the virus
- Minimizing stress in cats’ living environments
- Practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands and cleaning litter boxes regularly
- Isolating infected cats from healthy cats to prevent the spread of the virus
In conclusion, feline herpes eye infection is caused by the feline herpesvirus type 1 (FHV-1), which is highly contagious and can be transmitted through direct contact with an infected cat’s saliva, nasal secretions, or eye discharge. Cats that are housed in crowded or stressful environments and those with weakened immune systems are at higher risk of infection. While prevention is not always possible, steps can be taken to reduce the risk of infection and promote the health and well-being of cats.

How is feline herpes eye infection diagnosed?
Feline herpes eye infection can be challenging to diagnose because its signs and symptoms can be similar to those of other eye conditions. However, there are several diagnostic tests that veterinarians can perform to confirm the presence of the virus and rule out other causes of eye infection.
Physical examination
During a physical examination, the veterinarian will look for signs of eye infection, such as redness, discharge, and swelling of the eyelids. They will also check for other symptoms of the infection, such as sneezing and nasal discharge.
Fluorescein staining
Fluorescein staining is a simple diagnostic test that involves applying a fluorescent dye to the surface of the eye. The dye highlights any abnormalities, such as corneal ulcers or scratches, that may be present on the eye.
Viral culture
A viral culture involves taking a sample of eye discharge and testing it for the presence of the feline herpesvirus type 1 (FHV-1). This test can confirm the presence of the virus in cats with active infections.
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing
PCR testing is a highly sensitive diagnostic test that can detect the presence of viral DNA in a sample of eye discharge. This test is more sensitive than viral culture and can detect the virus in cats with both active and latent infections.
Why is an accurate diagnosis important?
An accurate diagnosis is important for determining the appropriate treatment for feline herpes eye infection. While antiviral medications can be effective in treating the virus, they are not always necessary or appropriate for all cats. An accurate diagnosis also helps to rule out other potential causes of eye infection and prevent unnecessary treatments.
In conclusion, diagnosing feline herpes eye infection can be challenging due to the similarity of its signs and symptoms to other eye conditions. However, diagnostic tests such as physical examination, fluorescein staining, viral culture, and PCR testing can help confirm the presence of the virus and rule out other causes of eye infection. An accurate diagnosis is important for determining the appropriate treatment and promoting the health and well-being of cats.

Treatment options for feline herpes eye infection
What are the treatment options for feline herpes eye infection?
The treatment options for feline herpes eye infection include:
Antiviral medications
Antibiotics
Antibiotics may be prescribed in cases where a secondary bacterial infection has developed due to the weakened immune system caused by the virus. These medications can help treat the bacterial infection and prevent further complications.
L-lysine supplements
Eye drops and ointments
How can feline herpes eye infection be managed?
Feline herpes eye infection can be managed by:
- Keeping the eyes clean and free from discharge
- Minimizing stress in the cat’s environment
- Providing a balanced and nutritious diet to support the immune system
- Isolating infected cats from healthy cats to prevent the spread of the virus
- Regular veterinary check-ups to monitor the cat’s health and well-being
In conclusion, treatment for feline herpes eye infection depends on the severity of the infection and the cat’s overall health. While there is no cure for the virus, several treatment options are available that can help manage the symptoms and prevent complications. Managing the infection involves keeping the eyes clean, minimizing stress, providing proper nutrition, and regular veterinary check-ups to ensure the cat’s health and well-being.
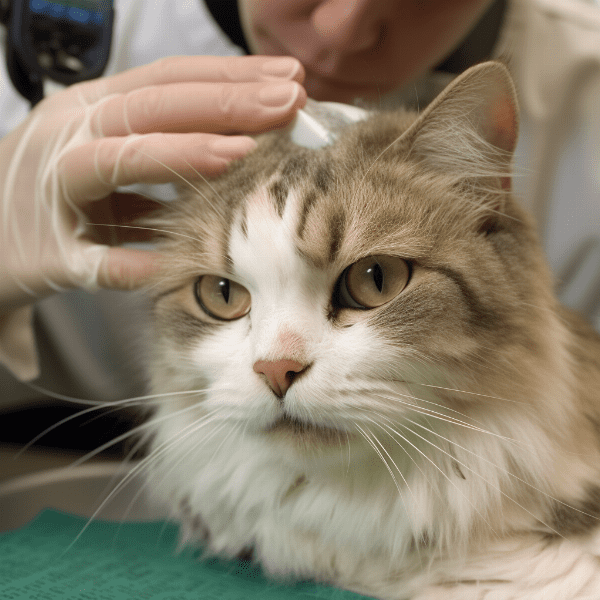
Preventing the spread of feline herpes eye infection
Feline herpes eye infection is highly contagious, and it is essential to take steps to prevent the spread of the virus to other cats.
How can feline herpes eye infection be transmitted?
Feline herpes eye infection can be transmitted from cat to cat through direct contact with an infected cat’s saliva, nasal secretions, or eye discharge. The virus can also be transmitted through contaminated objects, such as food and water dishes or litter boxes.
Isolate infected cats
Practice good hygiene
Practicing good hygiene can help prevent the spread of the virus. This includes washing hands thoroughly after handling infected cats and their belongings and cleaning litter boxes, food and water dishes, and bedding regularly.
Vaccination
Vaccination against feline herpesvirus type 1 (FHV-1) can help reduce the risk of infection. However, vaccination does not provide 100% protection against the virus.
Minimize stress
Stress can weaken a cat’s immune system and make them more susceptible to infection. Minimizing stress in cats’ living environments can help prevent the onset of feline herpes eye infection.
Can feline herpes eye infection be cured?
There is no cure for feline herpes eye infection, and infected cats can experience recurrent episodes throughout their lives. However, with proper management and treatment, the symptoms of the infection can be managed effectively.
In conclusion, preventing the spread of feline herpes eye infection is crucial to maintaining the health and well-being of cats. Steps can be taken to prevent the spread of the virus, including isolating infected cats, practicing good hygiene, vaccination, and minimizing stress in cats’ living environments. While there is no cure for the virus, proper management and treatment can effectively manage the symptoms and prevent complications.

Managing recurrent feline herpes eye infections
Feline herpes eye infection is a viral disease that can recur throughout a cat’s lifetime. Recurrent infections can be challenging to manage, but there are several strategies that can help reduce the frequency and severity of episodes.
Why do recurrent infections occur?
Recurrent feline herpes eye infections occur because the virus remains dormant in the cat’s body even after the initial infection has cleared. Stress, illness, and other factors can cause the virus to reactivate and cause another episode of infection.
What are the strategies for managing recurrent infections?
The following strategies can help manage recurrent feline herpes eye infections:
Antiviral medications
Antiviral medications, such as famciclovir and acyclovir, can help reduce the severity and duration of recurrent infections. These medications work by inhibiting the replication of the virus in the body.
L-lysine supplements
Stress reduction
Routine veterinary check-ups
Can recurrent infections be prevented?
While recurrent feline herpes eye infections cannot be prevented entirely, managing the infection effectively can help reduce the frequency and severity of episodes. Proper management includes antiviral medications, L-lysine supplements, stress reduction, and routine veterinary check-ups.
In conclusion, recurrent feline herpes eye infections can be challenging to manage, but several strategies can help reduce the frequency and severity of episodes. Antiviral medications, L-lysine supplements, stress reduction, and routine veterinary check-ups can all help manage the infection effectively. While recurrent infections cannot be prevented entirely, proper management can help improve the cat’s quality of life and promote their health and well-being.

Home care tips for cats with herpes eye infection
Home care is essential for cats with feline herpes eye infection to help manage the symptoms and promote their health and well-being. The following home care tips can help support cats with the infection.
Cleaning the eyes
Cleaning the eyes is an essential part of home care for cats with feline herpes eye infection. The eyes should be cleaned regularly with a warm, damp cloth to remove any discharge or crust that may accumulate. This can help prevent the spread of the virus and reduce the severity of symptoms.
Reducing stress
Stress can trigger the reactivation of the virus and lead to recurrent episodes of infection. Providing a calm and stable environment, regular exercise, and playtime can all help reduce stress in cats with the infection.
Nutritious diet
A nutritious diet is essential for supporting the immune system and promoting the health and well-being of cats with feline herpes eye infection. Feeding a balanced and complete diet that meets the cat’s nutritional needs can help support their immune system and reduce the severity of symptoms.
L-lysine supplements
L-lysine supplements can help reduce the frequency and severity of feline herpes eye infection. These supplements are readily available and can be added to the cat’s food or administered directly into the mouth.
Regular veterinary check-ups
Regular veterinary check-ups can help monitor the cat’s health and well-being and detect any signs of recurrent infections early. Early intervention can help prevent complications and reduce the severity of the infection.
Eye drops and ointments
In conclusion, home care is essential for managing feline herpes eye infection in cats. Cleaning the eyes regularly, reducing stress, providing a nutritious diet, L-lysine supplements, regular veterinary check-ups, isolation, and eye drops and ointments can all help manage the infection effectively and promote the cat’s health and well-being.

Complications of feline herpes eye infection
Feline herpes eye infection can lead to several complications, particularly if left untreated or poorly managed. The following are some of the potential complications that can arise from the infection.
Conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis is inflammation of the conjunctiva, the thin membrane that covers the eye and inner eyelid. It is a common complication of feline herpes eye infection and can cause redness, discharge, and discomfort.
Keratitis
Keratitis is inflammation of the cornea, the clear outer layer of the eye. It is a severe complication of feline herpes eye infection that can cause corneal scarring and vision loss.
Secondary bacterial infections
Feline herpes eye infection weakens the immune system, making cats more susceptible to secondary bacterial infections. These infections can lead to further complications and may require additional treatment.
Blindness
In severe cases, feline herpes eye infection can lead to blindness. This can occur due to corneal scarring, damage to the retina, or other complications that affect vision.
Prevention of complications
Prevention of complications involves prompt diagnosis and treatment of feline herpes eye infection, managing the infection effectively, and preventing the spread of the virus. Regular veterinary check-ups can help monitor the cat’s health and well-being and detect any signs of complications early.
In conclusion, feline herpes eye infection can lead to several complications if left untreated or poorly managed. Corneal ulcers, conjunctivitis, keratitis, secondary bacterial infections, and blindness are all potential complications of the infection. Prevention of complications involves prompt diagnosis and treatment, managing the infection effectively, and regular veterinary check-ups to monitor the cat’s health and well-being.

When to see a vet for feline herpes eye infection
Feline herpes eye infection can cause significant discomfort and lead to several complications if left untreated. It is essential to seek veterinary care promptly if you suspect your cat has the infection. The following are some signs that indicate when to see a vet for feline herpes eye infection.
Persistent symptoms
Persistent symptoms, such as redness, discharge, and squinting, indicate that the infection is not improving and may require veterinary attention.
Corneal ulcers
Corneal ulcers are a common complication of feline herpes eye infection and can be painful and lead to vision loss if left untreated. If you notice any signs of corneal ulcers, such as cloudiness, discharge, or redness, seek veterinary attention immediately.
Change in behavior
A change in behavior, such as lethargy, loss of appetite, or decreased activity, may indicate that the cat is in significant discomfort and requires veterinary attention.
Recurrent infections
Recurrent feline herpes eye infections can be challenging to manage and may require veterinary intervention to prevent complications and reduce the severity of episodes.
Complications
Complications of feline herpes eye infection, such as conjunctivitis, keratitis, and secondary bacterial infections, require prompt veterinary attention to prevent further complications and promote the cat’s health and well-being.
In conclusion
In conclusion, seeking veterinary care promptly is crucial if you suspect your cat has feline herpes eye infection. Persistent symptoms, corneal ulcers, changes in behavior, recurrent infections, and complications are all signs that indicate when to see a vet for the infection. Early intervention can help prevent complications, reduce the severity of the infection, and promote the cat’s health and well-being.