Table of Contents
- Understanding Feline Cataracts: An Introduction
- Common Causes of Feline Cataracts
- Recognizing the Symptoms of Feline Cataracts
- Diagnosing Feline Cataracts: What to Expect
- Treating Feline Cataracts: Medical and Surgical Options
- Preparing for Feline Cataract Surgery
- Caring for a Cat with Cataracts Post-Surgery
- Preventing and Managing Feline Cataracts
- Feline Cataracts and Your Cat’s Quality of Life
- Conclusion: Caring for Your Cat’s Eye Health
Understanding Feline Cataracts: An Introduction
Cataracts are a common condition that can affect cats of all ages and breeds. A cataract is an opacity in the lens of the eye that causes blurry vision and can eventually lead to blindness. Understanding the basics of feline cataracts is an important step in identifying and treating the condition early on.
Anatomy of the Eye
To understand how cataracts can affect a cat’s vision, it’s important to know the basic anatomy of the eye. The eye is a complex organ that has several components working together to allow animals to see. The cornea is the clear outer layer of the eye that helps to focus light. The iris is the colored part of the eye that controls the size of the pupil, which regulates the amount of light entering the eye. The lens is located behind the iris and is responsible for focusing light onto the retina. The retina is a layer of cells at the back of the eye that converts light into electrical signals that are sent to the brain.
How Cataracts Form
Cataracts form when the proteins in the lens of the eye clump together, causing opacities that interfere with vision. There are several reasons why this can happen, including genetics, aging, and injury. In some cases, cataracts may be caused by an underlying medical condition, such as diabetes.
Types of Cataracts
There are three main types of cataracts that can affect cats: nuclear, cortical, and posterior subcapsular. Nuclear cataracts are the most common type and occur in the center of the lens. Cortical cataracts form in the outer layer of the lens, while posterior subcapsular cataracts form at the back of the lens.
Risk Factors for Feline Cataracts
While cataracts can occur in cats of all ages and breeds, there are certain factors that can increase a cat’s risk of developing the condition. These include genetics, age, underlying medical conditions, and certain medications. It’s important for cat owners to be aware of these risk factors and to schedule regular eye exams with their veterinarian to catch any signs of cataracts early on.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the basics of feline cataracts is an important step in identifying and treating the condition early on. By knowing the anatomy of the eye, how cataracts form, the types of cataracts that can affect cats, and the risk factors for developing the condition, cat owners can take proactive steps to protect their pet’s eye health.

Common Causes of Feline Cataracts
While the exact cause of cataracts in cats is often unknown, there are several common factors that can increase a cat’s risk of developing the condition.
Genetics
Genetics can play a significant role in the development of cataracts in cats. Certain breeds, such as Persian and Siamese cats, are more prone to developing cataracts due to genetic predisposition. It’s important for breeders to test their cats for genetic disorders to reduce the risk of passing on these conditions to their offspring.
Aging
As cats age, the risk of developing cataracts increases. This is because the lens of the eye becomes less flexible and less able to repair itself over time. While cataracts can occur at any age, they are most commonly seen in older cats.
Trauma
Trauma to the eye can also lead to the development of cataracts. Injuries such as blunt force trauma or penetrating wounds can damage the lens, causing cloudiness and opacity.
Underlying Medical Conditions
Underlying medical conditions, such as diabetes and hypertension, can also increase a cat’s risk of developing cataracts. These conditions can cause changes in the lens of the eye that lead to cloudiness and opacity.
Medications
Certain medications, such as corticosteroids, can also increase the risk of cataract development in cats. It’s important to discuss any medications your cat may be taking with your veterinarian to ensure they are not contributing to the development of cataracts.
Conclusion
In conclusion, there are several common causes of feline cataracts, including genetics, aging, trauma, underlying medical conditions, and certain medications. By being aware of these risk factors, cat owners can take proactive steps to protect their pet’s eye health and catch any signs of cataracts early on. If you suspect your cat may be developing cataracts, it’s important to schedule an appointment with your veterinarian to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment options.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Feline Cataracts
Cataracts in cats can develop slowly over time, making it difficult for owners to notice any changes in their pet’s vision. However, there are several signs and symptoms that may indicate the presence of cataracts.
Changes in Eye Appearance
One of the most obvious signs of cataracts is a change in the appearance of the affected eye. The eye may appear cloudy, milky, or hazy, and the iris may appear different in color or shape.
Vision Changes
As cataracts progress, cats may also experience changes in their vision. They may bump into objects or have difficulty navigating their surroundings, especially in low light environments. Cats with cataracts may also be more hesitant to jump or climb, as they are unable to judge distances accurately.
Eye Discharge
In some cases, cats with cataracts may also experience eye discharge. The discharge may be clear, white, or yellow in color and can indicate an infection or inflammation in the eye.

Diagnosing Feline Cataracts: What to Expect
Physical Exam
During the physical exam, your veterinarian will examine your cat’s eyes and look for signs of cataracts, such as cloudiness, opacity, or changes in the appearance of the iris. They may also check your cat’s vision and examine their pupils for any abnormalities.
Eye Exam
Your veterinarian may also perform an eye exam to evaluate the internal structures of your cat’s eyes. This may include the use of specialized equipment, such as an ophthalmoscope, to examine the lens and retina of the eye.
Diagnostic Testing
In some cases, your veterinarian may recommend additional diagnostic testing to determine the underlying cause of your cat’s cataracts. This may include blood tests to evaluate for underlying medical conditions or genetic testing to identify any predispositions to cataract development.
Referral to a Veterinary Ophthalmologist
If your veterinarian suspects that your cat has cataracts or another eye condition that requires specialized treatment, they may refer you to a veterinary ophthalmologist. These specialists have advanced training in the diagnosis and treatment of eye conditions and can provide more specialized care for your cat.
Treating Feline Cataracts: Medical and Surgical Options
Medical Management
In some cases, medical management may be used to manage the symptoms of cataracts and slow their progression. This may include the use of topical medications, such as anti-inflammatory drops, to reduce inflammation and discomfort in the eye.
Surgery
Surgery is the most effective treatment option for cats with cataracts, particularly if the cataracts are causing significant vision impairment. During cataract surgery, the clouded lens is removed and replaced with an artificial lens implant. The surgery is performed under general anesthesia and requires specialized equipment and training.
Preparing for Surgery
If your cat requires cataract surgery, there are several steps you can take to help prepare them for the procedure. This may include preoperative testing, such as blood work and cardiac evaluation, to ensure that your cat is healthy enough for surgery. You may also need to make modifications to your cat’s diet and medication regimen in the days leading up to surgery.
Post-Surgical Care
After cataract surgery, your cat will require specialized post-surgical care to ensure a successful recovery. This may include the use of topical medications, such as antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drops, to reduce the risk of infection and promote healing. Your veterinarian will provide detailed instructions for caring for your cat post-surgery, including instructions for medication administration, activity restrictions, and follow-up appointments.
Conclusion
In conclusion, there are several treatment options available for cats with cataracts, including medical management and surgery. If your cat requires cataract surgery, it’s important to prepare them properly and provide appropriate post-surgical care to ensure a successful recovery. By working closely with your veterinarian and following their recommendations, you can help improve your cat’s vision and overall quality of life.
Preparing for Feline Cataract Surgery
Preoperative Testing
Before surgery, your veterinarian may recommend preoperative testing to ensure that your cat is healthy enough for the procedure. This may include blood work to evaluate organ function and cardiac evaluation to assess your cat’s heart health.
Medication Management
In the days leading up to surgery, your veterinarian may recommend modifications to your cat’s medication regimen. It’s important to follow these instructions carefully to ensure that your cat is not taking any medications that could interfere with the surgery or postoperative care.
Dietary Changes
Your veterinarian may also recommend dietary changes in the days leading up to surgery to ensure that your cat is properly hydrated and has the nutrients needed for a successful recovery.
Anesthesia Protocol
Cataract surgery is performed under general anesthesia, which carries some inherent risks. Your veterinarian will carefully select an anesthesia protocol that is appropriate for your cat’s health status and will closely monitor them during the procedure to ensure their safety.
Follow-Up Care
After surgery, your cat will require specialized postoperative care to ensure a successful recovery. This may include the use of topical medications, such as antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drops, and activity restrictions to prevent complications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, preparing your cat for cataract surgery requires careful planning and preparation. By following your veterinarian’s recommendations for preoperative testing, medication management, and dietary changes, you can help ensure a successful outcome. With proper preparation and postoperative care, your cat can enjoy improved vision and a better quality of life.

Caring for a Cat with Cataracts Post-Surgery
After cataract surgery, your cat will require specialized postoperative care to ensure a successful recovery. Here are some important steps you can take to care for your cat after surgery.
Medication Administration
Your veterinarian will prescribe medications, such as antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drops, to help prevent infection and promote healing after surgery. It’s important to follow their instructions carefully and administer the medications as directed.
Activity Restrictions
After surgery, your cat may need to be restricted from certain activities to prevent complications. This may include limiting jumping or running and keeping them in a quiet, calm environment to promote healing.
Follow-Up Appointments
Your cat will require follow-up appointments with your veterinarian to monitor their healing progress and ensure that their vision is improving. It’s important to attend these appointments and follow your veterinarian’s recommendations for postoperative care.
Nutrition and Hydration
Proper nutrition and hydration are essential for a successful recovery after surgery. Your veterinarian may recommend a specialized diet or increased water intake to support your cat’s healing process.
Conclusion
In conclusion, caring for a cat with cataracts after surgery requires specialized postoperative care and follow-up appointments. By administering medications as directed, restricting your cat’s activity as needed, making environmental modifications, and ensuring proper nutrition and hydration, you can help ensure a successful recovery and improved vision for your cat.
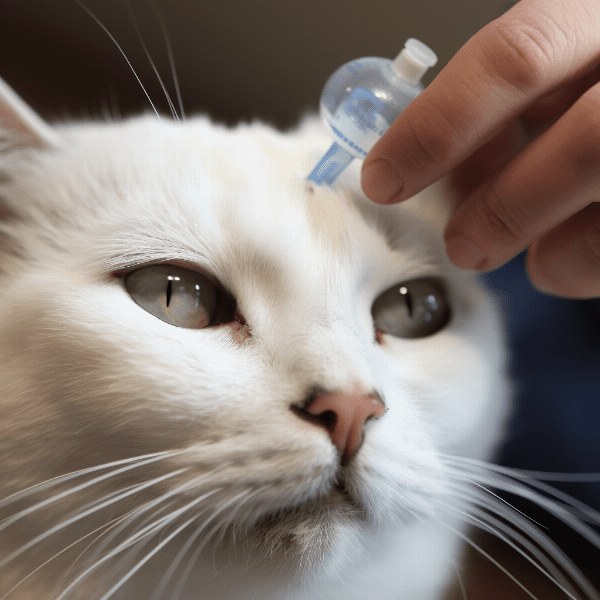

Preventing and Managing Feline Cataracts
While not all cases of feline cataracts can be prevented, there are several steps you can take to reduce your cat’s risk of developing the condition and manage it if it does occur.
Regular Eye Exams
Regular eye exams are an important part of maintaining your cat’s eye health and detecting any changes early on. Your veterinarian can perform a comprehensive eye exam and recommend any necessary preventative measures or treatment options.
Genetic Testing
If you plan to breed your cat, genetic testing can help identify any predispositions to genetic disorders, including cataracts. By selecting breeding pairs with a lower risk of genetic disorders, you can help reduce the risk of passing on these conditions to their offspring.
Managing Underlying Medical Conditions
Underlying medical conditions, such as diabetes and hypertension, can increase a cat’s risk of developing cataracts. It’s important to manage these conditions carefully with the help of your veterinarian to reduce the risk of cataract development.
Environmental Modifications
If your cat has already developed cataracts, making modifications to their environment can help them adjust to their new vision. This may include providing additional lighting, avoiding sudden changes in their surroundings, and reducing obstacles in their path.
Proper Nutrition and Hydration
Proper nutrition and hydration are essential for maintaining your cat’s overall health and eye health. Your veterinarian can recommend a balanced diet and hydration plan to support your cat’s eye health.
Conclusion
In conclusion, preventing and managing feline cataracts requires a combination of preventative measures and careful management of underlying medical conditions. By working closely with your veterinarian and providing your cat with the proper care and support, you can help reduce their risk of developing cataracts and improve their overall eye health.

Feline Cataracts and Your Cat’s Quality of Life
Cataracts can significantly impact your cat’s quality of life, affecting their vision, mobility, and behavior. However, with proper diagnosis and treatment, many cats with cataracts can still lead happy, healthy lives.
Vision Impairment
Cataracts can cause significant vision impairment, making it difficult for cats to navigate their surroundings and engage in normal activities. However, with prompt diagnosis and treatment, many cats can regain their vision and resume normal activities.
Mobility Issues
Cats with cataracts may also experience mobility issues, such as difficulty jumping or climbing. However, with environmental modifications and proper management, many cats can continue to engage in these activities with minimal difficulty.
Behavioral Changes
Cats with cataracts may also exhibit behavioral changes, such as increased vocalization, clinginess, or irritability. These changes may be related to their discomfort or frustration with changes in their vision. With proper diagnosis and treatment, many of these behavioral changes can be addressed and managed effectively.
Treatment Options
There are several treatment options available for cats with cataracts, including medical management and surgery. The best treatment option for your cat will depend on several factors, such as the severity of the cataracts and the underlying cause. With proper treatment, many cats with cataracts can regain their vision and resume normal activities.
Conclusion
In conclusion, feline cataracts can significantly impact your cat’s quality of life, but with proper diagnosis and treatment, many cats can still lead happy, healthy lives. If you suspect that your cat may have cataracts, it’s important to schedule an appointment with your veterinarian as soon as possible. Early detection and treatment can help preserve your cat’s vision and improve their overall quality of life.

Conclusion: Caring for Your Cat’s Eye Health
Caring for your cat’s eye health is an essential part of maintaining their overall health and wellbeing. Regular eye exams, proper nutrition and hydration, and management of underlying medical conditions can all help reduce the risk of feline cataracts and other eye conditions.
If you suspect that your cat may be experiencing vision changes or developing cataracts, it’s important to schedule an appointment with your veterinarian for a thorough eye examination. Early detection and treatment can help preserve your cat’s vision and improve their overall quality of life.
If your cat does require cataract surgery, it’s important to carefully follow your veterinarian’s recommendations for preoperative and postoperative care to ensure a successful outcome. With proper care and support, many cats with cataracts can regain their vision and continue to lead happy, healthy lives.
In conclusion, by working closely with your veterinarian and providing your cat with the proper care and support, you can help ensure optimal eye health and overall wellbeing for your feline friend.




