Table of Contents
- Understanding Feline Diabetes
- The Importance of Glucose Monitoring for Cats
- Types of Feline Glucose Monitors
- How to Monitor Your Cat’s Glucose Levels at Home
- Interpreting Your Cat’s Glucose Readings
- Diet and Exercise for Diabetic Cats
- Medications for Feline Diabetes
- When to Consult with Your Veterinarian
- Troubleshooting Common Issues with Feline Glucose Monitoring
- The Benefits of Regular Feline Glucose Monitoring
Understanding Feline Diabetes
Feline diabetes is a chronic disease that affects cats of all ages and breeds. It occurs when a cat’s body is unable to produce or properly use insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels. Without insulin, the cat’s blood sugar levels become too high, leading to a range of health problems.
The Causes of Feline Diabetes
The exact causes of feline diabetes are not fully understood, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Some studies suggest that certain breeds, such as Burmese and Siamese cats, are more prone to developing the disease. Other risk factors include obesity, a sedentary lifestyle, and a high-carbohydrate diet.
The Symptoms of Feline Diabetes
The symptoms of feline diabetes can vary from cat to cat, but common signs include increased thirst and urination, weight loss, lethargy, and a poor coat condition. Some cats may also experience increased hunger, vomiting, or even blindness if the disease is left untreated.
The Diagnosis of Feline Diabetes
If you suspect your cat may have diabetes, it’s important to consult with a veterinarian. The vet will typically perform a physical exam and blood and urine tests to diagnose the disease. They may also recommend monitoring your cat’s blood glucose levels at home using a glucose monitor.
The Effects of Feline Diabetes
If left untreated, feline diabetes can have serious health consequences for your cat. High blood sugar levels can damage organs and tissues over time, leading to conditions such as neuropathy, kidney disease, and even coma. However, with proper treatment and management, many cats with diabetes can lead happy and healthy lives.

The Importance of Glucose Monitoring for Cats
Glucose monitoring is a crucial part of managing feline diabetes. By regularly checking your cat’s blood sugar levels, you can ensure that their treatment plan is working effectively and make any necessary adjustments. Here are some reasons why glucose monitoring is so important for cats with diabetes.
Avoiding Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar, can occur in diabetic cats that are receiving insulin treatment. This can cause seizures, weakness, and even coma in severe cases. Glucose monitoring can help you detect hypoglycemia early and take steps to correct it before it becomes a serious problem.
Adjusting Insulin Dosages
The correct insulin dosage for a diabetic cat can vary depending on factors such as their weight, diet, and activity level. Regular glucose monitoring can help you determine whether your cat’s insulin dosage needs to be adjusted. This can prevent blood sugar fluctuations that can cause long-term health problems.
Identifying Trends
By tracking your cat’s blood sugar levels over time, you can identify trends and patterns that may indicate changes in their condition. For example, if your cat’s blood sugar levels are consistently high in the morning, it may indicate that their insulin dosage needs to be increased.
Ensuring Long-Term Health
Feline diabetes is a chronic disease that requires lifelong management. Regular glucose monitoring can help ensure that your cat’s diabetes is well-controlled, which can prevent long-term health complications such as kidney disease and neuropathy.
Overall, glucose monitoring is an essential part of managing feline diabetes. It allows you to take an active role in your cat’s health and ensure that they are receiving the best possible care.

Types of Feline Glucose Monitors
There are several types of glucose monitors that can be used to monitor your cat’s blood sugar levels at home. Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages, so it’s important to choose the one that works best for you and your cat. Here are some of the most common types of feline glucose monitors.
Blood Glucose Meters
Blood glucose meters are the most commonly used type of glucose monitor for cats. They require a small blood sample, usually obtained by pricking the cat’s ear or paw pad with a lancet. The blood sample is then placed on a test strip, which is inserted into the meter to obtain a reading. Some meters require calibration with a control solution, while others are factory-calibrated.
Continuous Glucose Monitors
Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) are a newer type of glucose monitor that can provide more comprehensive data than traditional meters. CGMs use a small sensor that is inserted under the cat’s skin to measure their blood sugar levels continuously. The sensor sends this data to a receiver or smartphone app, which can provide real-time glucose readings and alerts if levels become too high or too low.
Urine Glucose Test Strips
Urine glucose test strips are another option for monitoring your cat’s blood sugar levels. These strips are dipped into a urine sample and change color to indicate the presence of glucose. While they are less invasive than blood glucose meters, urine glucose test strips are not as accurate and can be affected by factors such as hydration levels and time of day.
Non-Invasive Glucose Monitors
Non-invasive glucose monitors are still in development and are not yet widely available for home use. These monitors use methods such as spectroscopy or fluorescence to measure glucose levels without the need for a blood sample. While they may offer a more comfortable and convenient option for cats, they are not yet as accurate as traditional glucose monitors.
Overall, the type of glucose monitor you choose will depend on your cat’s needs and your personal preferences. It’s important to work with your veterinarian to choose the monitor that will work best for you and your cat.

How to Monitor Your Cat’s Glucose Levels at Home
Monitoring your cat’s glucose levels at home is an important part of managing their diabetes. Here are some steps you can take to monitor your cat’s blood sugar levels at home.
Step 1: Choose a Glucose Monitor
As discussed in the previous section, there are several types of glucose monitors available for cats. Choose the one that works best for you and your cat based on factors such as accuracy, convenience, and cost.
Step 2: Gather Supplies
You will need the following supplies to monitor your cat’s blood sugar levels at home:
- Glucose monitor
- Test strips (if using a blood glucose meter)
- Lancet (if using a blood glucose meter)
- Alcohol swabs
- Cotton balls
- Treats (optional)
Step 3: Prepare Your Cat
Before you begin monitoring your cat’s blood sugar levels, make sure they are comfortable and relaxed. Offer treats or play with them for a few minutes to help them relax.
Step 4: Obtain a Blood Sample
If you are using a blood glucose meter, you will need to obtain a small blood sample from your cat. The ear or paw pad are common areas to obtain a sample. Use an alcohol swab to clean the area, then use a lancet to prick the skin and obtain a small drop of blood. Touch the test strip to the blood drop and insert it into the glucose meter to obtain a reading.
Step 5: Record the Results
Record the results of each glucose reading in a logbook or on a spreadsheet. This will allow you to track your cat’s glucose levels over time and identify any trends or patterns.
Step 6: Consult with Your Veterinarian
It’s important to consult with your veterinarian regularly to ensure that your cat’s diabetes is well-controlled. Your vet can review your glucose monitoring logs and make any necessary adjustments to your cat’s treatment plan.
Overall, monitoring your cat’s blood sugar levels at home can help ensure that their diabetes is well-controlled and prevent long-term health complications. With the right tools and preparation, monitoring your cat’s glucose levels can be a simple and routine part of their care.

Interpreting Your Cat’s Glucose Readings
Interpreting your cat’s glucose readings is an important part of monitoring their diabetes. Here are some factors to consider when interpreting your cat’s glucose readings.
Understanding Glucose Levels
Normal glucose levels in cats typically range from 60-160 mg/dL. However, the target glucose range for a diabetic cat may be different depending on factors such as their age, weight, and overall health. Consult with your veterinarian to determine your cat’s target glucose range.
Time of Day
Blood glucose levels can fluctuate throughout the day, so it’s important to take readings at consistent times each day. Your veterinarian may recommend taking readings before meals, before insulin injections, or at other specific times.
Exercise and Activity Level
Exercise and activity level can also affect your cat’s glucose levels. If your cat’s glucose levels are consistently high after periods of activity, it may indicate that their insulin dosage needs to be adjusted.
Adjusting Treatment Plan
Overall, interpreting your cat’s glucose readings requires careful attention to their diet, activity level, and overall health. By monitoring your cat’s glucose levels and working closely with your veterinarian, you can help ensure that their diabetes is well-controlled and prevent long-term health complications.
Diet and Exercise for Diabetic Cats
Diet and exercise are important factors in managing feline diabetes. Here are some guidelines for managing your diabetic cat’s diet and exercise routine.
Diet
A high-protein, low-carbohydrate diet is recommended for diabetic cats. Carbohydrates are converted into glucose in the body, so limiting carbohydrate intake can help regulate blood sugar levels. Consult with your veterinarian to determine the best diet for your cat.
Feeding Schedule
Feeding your cat on a consistent schedule can help regulate their blood sugar levels. Divide their daily food intake into several small meals throughout the day, rather than feeding them one or two large meals.
Portion Control
Portion control is important for managing your cat’s weight and blood sugar levels. Consult with your veterinarian to determine the appropriate portion sizes for your cat’s age, weight, and activity level.
Exercise
Regular exercise can help regulate your cat’s blood sugar levels and maintain a healthy weight. Encourage your cat to engage in activities such as playing with toys or climbing on a cat tree. Aim for at least 10-15 minutes of activity per day.
Monitoring
Regularly monitoring your cat’s weight and glucose levels can help determine whether their diet and exercise routine is working effectively. Consult with your veterinarian to determine how often to monitor your cat’s weight and glucose levels.

Medications for Feline Diabetes
Insulin is the primary medication used to treat feline diabetes. Here are some guidelines for administering insulin to your cat.
Types of Insulin
There are several types of insulin available for cats, including rapid-acting, intermediate-acting, and long-acting insulin. Consult with your veterinarian to determine the best type of insulin for your cat’s individual needs.
Administration
Insulin is typically administered via injection under the skin, using a syringe or insulin pen. Your veterinarian can demonstrate how to properly administer insulin to your cat. It’s important to administer insulin at consistent times each day and to rotate injection sites to prevent irritation.
Dosage
The correct insulin dosage for your cat will depend on factors such as their weight, diet, and activity level. Your veterinarian will determine the appropriate dosage and may adjust it over time based on your cat’s glucose readings.
Other Medications
In addition to insulin, other medications may be prescribed to manage feline diabetes. These may include oral medications such as glipizide or dietary supplements such as omega-3 fatty acids.
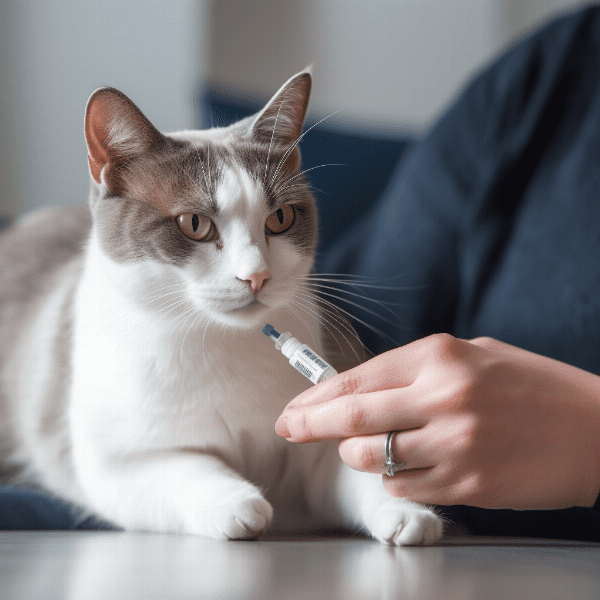

When to Consult with Your Veterinarian
Managing feline diabetes requires regular communication and collaboration with your veterinarian. Here are some situations when it’s important to consult with your veterinarian.
Glucose Readings Outside of Target Range
If your cat’s glucose readings are consistently outside of their target range, it may indicate that their treatment plan needs to be adjusted. Consult with your veterinarian to determine the best course of action.
Changes in Behavior or Appetite
Changes in your cat’s behavior or appetite may indicate a problem with their diabetes management. Contact your veterinarian if you notice any changes in your cat’s behavior or appetite.
Side Effects from Medications
Side effects from insulin or other medications can be serious. If your cat experiences any side effects, contact your veterinarian immediately.
Illness or Injury
Illness or injury can affect your cat’s glucose levels and diabetes management. Contact your veterinarian if your cat becomes ill or injured.
Regular Check-Ups
Regular check-ups with your veterinarian are important for managing feline diabetes. Your veterinarian can monitor your cat’s glucose levels and make any necessary adjustments to their treatment plan.
Overall, regular communication with your veterinarian is crucial for managing feline diabetes. By staying in touch with your veterinarian and reporting any changes in your cat’s health, you can help ensure that their diabetes is well-controlled and prevent long-term health complications.

Troubleshooting Common Issues with Feline Glucose Monitoring
Monitoring your cat’s glucose levels can be challenging at times. Here are some common issues with feline glucose monitoring and how to troubleshoot them.
Inconsistent Readings
If your cat’s glucose readings are inconsistent, it may be due to factors such as incorrect handling of the glucose monitor, expired test strips, or a problem with the meter itself. Check the glucose monitor’s instructions and consult with your veterinarian if the issue persists.
Stress
Stress can affect your cat’s glucose levels and make monitoring more difficult. Try to keep your cat calm and relaxed during glucose monitoring, and consider using treats or toys to distract them.
Blood Sample Difficulties
Obtaining a blood sample from your cat can be challenging. If you’re having trouble obtaining a sample, try using a different area such as the other ear or paw pad. You can also try warming the area with a warm towel or offering treats to distract your cat.
Meter Error Messages
If you receive an error message from your glucose monitor, consult the instruction manual for troubleshooting tips. If the issue persists, contact the manufacturer or your veterinarian for assistance.
False Readings
False readings can occur if the glucose monitor is not properly calibrated or if there is a problem with the test strip. Check the monitor’s instructions for calibration tips, and consider using a control solution to confirm accurate readings.
Overall, troubleshooting issues with feline glucose monitoring requires attention to detail and patience. By working closely with your veterinarian and following the monitor’s instructions, you can help ensure accurate and consistent glucose readings for your cat.

The Benefits of Regular Feline Glucose Monitoring
Regular monitoring of your cat’s glucose levels can have numerous benefits for their health and well-being. Here are some of the benefits of regular feline glucose monitoring.
Early Detection of Problems
Regular monitoring allows for early detection of problems with your cat’s diabetes management, such as high or low blood sugar levels. Early detection allows for prompt intervention and adjustment of treatment plans, which can help prevent long-term health complications.
Improved Diabetes Management
Regular monitoring can help ensure that your cat’s diabetes is well-controlled, which can improve their overall health and quality of life. By monitoring glucose levels and making adjustments to treatment plans as needed, you can help prevent complications such as neuropathy, kidney disease, and blindness.
Better Communication with Your Veterinarian
Regular monitoring requires regular communication with your veterinarian, which can improve the overall quality of care for your cat. By staying in touch with your veterinarian and reporting any changes in your cat’s health or behavior, you can work together to ensure that your cat’s diabetes management is optimized.
Increased Confidence in Managing Diabetes
Regular monitoring can increase your confidence in managing your cat’s diabetes. By understanding how to use a glucose monitor and interpret glucose readings, you can feel more empowered in managing your cat’s health.
Overall, regular feline glucose monitoring can have numerous benefits for your cat’s health and well-being. By staying proactive and working closely with your veterinarian, you can help ensure that your cat’s diabetes is well-controlled and prevent long-term health complications.