Table of Contents
- Understanding Feline Diabetes: Causes and Symptoms
- Diagnosing Feline Diabetes: Tests and Procedures
- Treating Feline Diabetes: Medications and Lifestyle Changes
- Monitoring Your Cat’s Blood Sugar: Tips and Techniques
- Preventing Complications of Feline Diabetes
- Nutrition for Cats with Diabetes: What to Feed and What to Avoid
- Exercise and Playtime for Cats with Diabetes
- Working with Your Vet: Collaborating for Your Cat’s Health
- Living with a Diabetic Cat: Coping Strategies and Emotional Support.
Understanding Feline Diabetes: Causes and Symptoms
Feline diabetes is a common condition that affects many cats, especially those that are middle-aged or older. It occurs when a cat’s body is unable to produce or effectively use insulin, which is a hormone that regulates the body’s blood sugar levels. Without adequate insulin, a cat’s blood sugar levels can become too high, which can lead to a range of health problems.
Causes of Feline Diabetes
The exact causes of feline diabetes are not fully understood, but there are several factors that may contribute to the development of the condition. These include:
- Obesity: Overweight cats are at a higher risk of developing diabetes, as excess body fat can make it more difficult for the body to produce and use insulin effectively.
- Genetics: Certain breeds of cats, such as Burmese and Siamese cats, are more prone to developing diabetes than others. This suggests that genetics may play a role in the development of the condition.
- Age: Feline diabetes is more common in cats that are middle-aged or older, as the body’s ability to produce and use insulin decreases with age.
Symptoms of Feline Diabetes
It’s important to be aware of the symptoms of feline diabetes so that you can recognize the condition and seek treatment for your cat as soon as possible. Some common symptoms of feline diabetes include:
- Increased thirst: Cats with diabetes may drink more water than usual, as the body tries to flush out excess sugar in the blood.
- Frequent urination: Increased urination is a common symptom of diabetes, as the body tries to eliminate excess sugar through the urine.
- Weight loss: Despite an increased appetite, cats with diabetes may lose weight as the body breaks down fat and muscle tissue for energy.
- Lethargy: Cats with diabetes may be less active than usual and may seem to lack energy or enthusiasm for play.
- Vomiting and diarrhea: Some cats with diabetes may experience gastrointestinal symptoms such as vomiting and diarrhea.
If you notice any of these symptoms in your cat, it’s important to schedule a veterinary appointment as soon as possible. Early diagnosis and treatment can help manage the condition and prevent complications.

Diagnosing Feline Diabetes: Tests and Procedures
If you suspect that your cat may have diabetes based on their symptoms, your veterinarian will need to perform some tests to confirm the diagnosis. This section will cover the different tests and procedures used to diagnose feline diabetes.
Physical Examination
The first step in diagnosing feline diabetes is a physical examination by your veterinarian. During this exam, your vet will look for signs of diabetes such as weight loss, increased thirst and urination, and lethargy. They will also perform a thorough examination of your cat’s overall health, checking their heart rate, blood pressure, and body temperature.
Blood Tests
Blood tests are the most common way to diagnose feline diabetes. These tests measure your cat’s blood sugar levels and can also detect other abnormalities that may be contributing to their symptoms. Your vet may perform one or more of the following blood tests:
- Blood glucose test: This test measures the amount of glucose (sugar) in your cat’s blood. High levels of glucose can indicate diabetes.
- Fructosamine test: This test measures the average blood glucose level over the past two to three weeks. It is used to diagnose diabetes in cats that have recently eaten or have other conditions that may affect their blood sugar levels.
- Complete blood count (CBC): This test measures the number and types of blood cells in your cat’s blood. Anemia and other blood abnormalities can contribute to diabetes symptoms.
Urine Tests
Urine tests can also be used to diagnose feline diabetes. These tests measure the amount of glucose and ketones (byproducts of fat breakdown) in your cat’s urine. Your vet may perform one or more of the following urine tests:
- Urinalysis: This test examines your cat’s urine for the presence of glucose, ketones, and other substances that may indicate diabetes.
- Urine culture: This test checks for the presence of bacteria in your cat’s urine, which can cause urinary tract infections that can worsen diabetes symptoms.
If your cat is diagnosed with diabetes, your veterinarian may perform additional tests to assess their overall health and determine the best course of treatment.

Treating Feline Diabetes: Medications and Lifestyle Changes
If your cat is diagnosed with diabetes, there are several treatment options available to manage the condition. This section will cover the medications and lifestyle changes that can help your cat live a happy and healthy life with diabetes.
Insulin Therapy
Insulin therapy is the primary treatment for feline diabetes. This involves giving your cat regular injections of insulin to regulate their blood sugar levels. Your veterinarian will determine the type and dosage of insulin that your cat needs based on their weight, age, and other factors. You will need to administer the insulin injections at home, following your vet’s instructions carefully.
Prescription Diets
Prescription diets are another important aspect of managing feline diabetes. These diets are formulated to provide balanced nutrition while helping to regulate your cat’s blood sugar levels. Prescription diets are typically low in carbohydrates and high in protein, which can help your cat maintain a healthy weight and reduce the risk of complications from diabetes.
Exercise
Regular exercise is important for cats with diabetes. Exercise can help your cat maintain a healthy weight and improve their insulin sensitivity. You can encourage your cat to exercise by playing with them, providing toys to play with, and creating an engaging and stimulating environment for them.
Blood Glucose Monitoring
Monitoring your cat’s blood glucose levels is an important part of managing feline diabetes. You can monitor your cat’s blood glucose levels at home using a glucometer and test strips. Your veterinarian will teach you how to use these tools and how to interpret the results.
Managing Stress
Stress can have a negative impact on your cat’s health and can worsen diabetes symptoms. You can help your cat manage stress by providing a calm and stable environment, creating a routine for feeding and exercise, and using calming techniques such as massage and aromatherapy.
With proper treatment and management, cats with diabetes can live long and happy lives. Work closely with your veterinarian to develop a treatment plan that meets your cat’s unique needs and lifestyle.
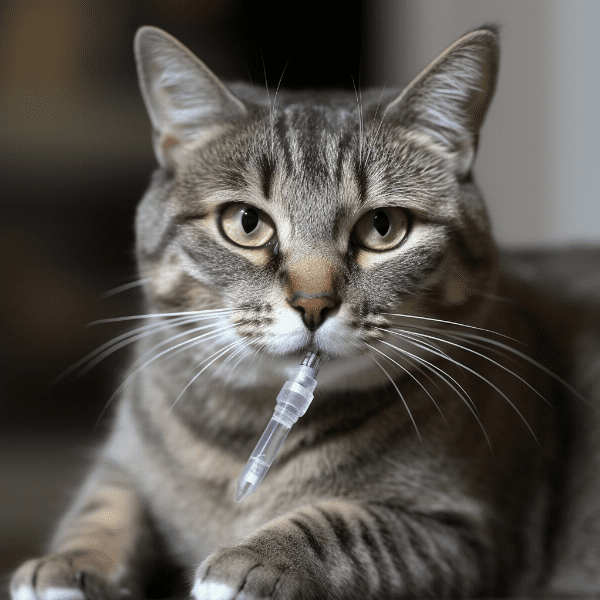

Monitoring Your Cat’s Blood Sugar: Tips and Techniques
Monitoring your cat’s blood sugar levels is an essential part of managing feline diabetes. This section will cover some tips and techniques for monitoring your cat’s blood sugar at home.
Using a Glucometer
A glucometer is a device that measures your cat’s blood sugar levels. You can purchase a glucometer from your veterinarian or a pet supply store, and your vet will teach you how to use it. To use a glucometer, you will need to prick your cat’s ear or paw to obtain a small sample of blood, which you will then place on a test strip. The glucometer will then give you a reading of your cat’s blood sugar levels.
Establishing a Monitoring Routine
Establishing a routine for monitoring your cat’s blood sugar levels can help you stay on top of their diabetes management. Your veterinarian will advise you on how often to monitor your cat’s blood sugar levels based on their individual needs. In general, it’s recommended to check your cat’s blood sugar levels at least once a day, preferably at the same time each day.
Keeping a Log
Keeping a log of your cat’s blood sugar levels can help you and your veterinarian track their progress and adjust their treatment plan as needed. You can use a notebook or a smartphone app to record your cat’s blood sugar levels, along with any notes about their behavior, diet, and exercise.
Identifying Patterns and Trends
Monitoring your cat’s blood sugar levels over time can help you identify patterns and trends that may indicate a need for a change in their treatment plan. For example, if you notice that your cat’s blood sugar levels are consistently high in the morning, you may need to adjust their insulin dosage or feeding schedule.
Working with Your Veterinarian
Monitoring your cat’s blood sugar levels is an important part of managing feline diabetes, but it’s also important to work closely with your veterinarian to ensure that your cat is receiving the best possible care. Your vet can help you interpret your cat’s blood sugar readings and make adjustments to their treatment plan as needed.
By monitoring your cat’s blood sugar levels regularly and working closely with your veterinarian, you can help manage your cat’s diabetes and ensure that they stay healthy and happy.
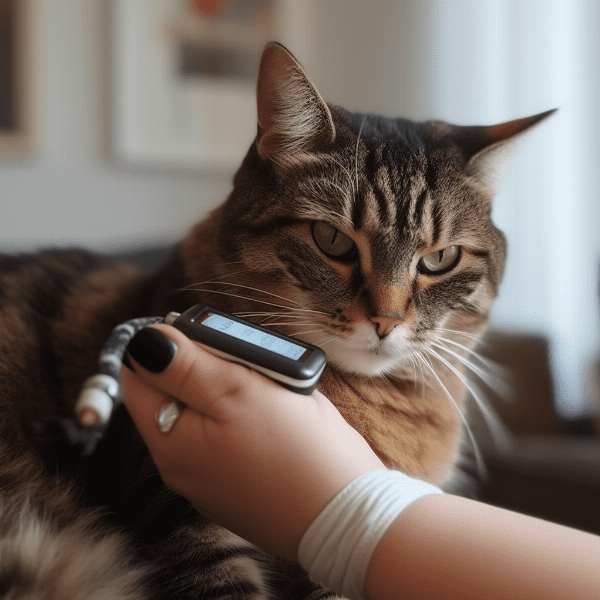

Preventing Complications of Feline Diabetes
While feline diabetes can be managed with proper treatment and care, it can also lead to a range of health complications if left untreated. This section will cover some tips for preventing complications of feline diabetes.
Preventing Infections
Cats with diabetes are at a higher risk of developing infections, especially urinary tract infections and skin infections. To prevent infections, it’s important to keep your cat’s litter box clean and to monitor their skin for any signs of irritation or infection. If you notice any signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or discharge, contact your veterinarian right away.
Managing Weight and Diet
Maintaining a healthy weight and diet is important for preventing complications of feline diabetes. Obesity can make it more difficult to manage diabetes, so it’s important to work with your veterinarian to develop a diet and exercise plan that meets your cat’s individual needs.
Managing Blood Sugar Levels
Maintaining consistent blood sugar levels is key to preventing complications of feline diabetes. Work with your veterinarian to develop a treatment plan that includes regular blood glucose monitoring, insulin therapy, and any necessary lifestyle changes.
Dental Care
Cats with diabetes are at a higher risk of developing dental problems, such as gum disease and tooth decay. To prevent dental problems, it’s important to brush your cat’s teeth regularly, provide them with dental treats and toys, and schedule regular dental cleanings with your veterinarian.
By taking steps to prevent complications of feline diabetes, you can help ensure that your cat stays healthy and happy. Work closely with your veterinarian to develop a comprehensive diabetes management plan that meets your cat’s individual needs.

Nutrition for Cats with Diabetes: What to Feed and What to Avoid
Proper nutrition is essential for managing feline diabetes. This section will cover what to feed and what to avoid when it comes to nutrition for cats with diabetes.
High-Protein, Low-Carbohydrate Diets
High-protein, low-carbohydrate diets are recommended for cats with diabetes. Protein helps maintain muscle mass and can help regulate blood sugar levels, while carbohydrates can cause blood sugar spikes. Prescription diets formulated specifically for cats with diabetes are available from your veterinarian.
Wet vs. Dry Food
Wet food is generally recommended for cats with diabetes, as it has a higher moisture content and can help prevent dehydration. Dry food is often higher in carbohydrates and can cause blood sugar spikes. However, if your cat prefers dry food, there are prescription diets available that are formulated specifically for cats with diabetes.
Avoid High-Carbohydrate Foods
High-carbohydrate foods should be avoided when feeding cats with diabetes. This includes foods such as rice, potatoes, and corn. These foods can cause blood sugar spikes and make it more difficult to regulate your cat’s blood sugar levels.
Avoid Treats and Table Scraps
Treats and table scraps should be avoided or given in moderation when feeding cats with diabetes. Many treats and table scraps are high in carbohydrates and can cause blood sugar spikes. Stick to small amounts of low-carbohydrate treats or try using small pieces of cooked chicken or turkey as a treat.
Feeding Schedule
Establishing a regular feeding schedule can help regulate your cat’s blood sugar levels. Your veterinarian can recommend a feeding schedule that meets your cat’s individual needs. It’s important to stick to the feeding schedule and avoid free-feeding your cat, as this can cause blood sugar spikes.
Exercise and Playtime for Cats with Diabetes
Regular exercise and playtime are important for cats with diabetes. Exercise can help your cat maintain a healthy weight, improve their insulin sensitivity, and reduce stress. This section will cover some tips for exercise and playtime for cats with diabetes.
Create an Enriching Environment
Creating an enriching environment for your cat can encourage them to be more active and engaged. Provide your cat with toys, scratching posts, and climbing structures to stimulate their natural instincts. Consider rotating toys and changing their location to keep your cat interested and engaged.
Interactive Playtime
Interactive playtime with your cat can provide exercise and mental stimulation. Try playing with toys that encourage your cat to chase and pounce, such as a feather wand or a laser pointer. Be sure to provide plenty of breaks and avoid overexerting your cat.
Encourage Movement
Encouraging your cat to move throughout the day can provide exercise and help regulate their blood sugar levels. Try placing their food and water dishes in different locations to encourage movement. Consider using puzzle feeders or food dispensers to make mealtime more interactive.
Regular Exercise
Regular exercise is important for cats with diabetes. This can include structured exercise such as playtime, as well as unstructured exercise such as climbing and exploring. Aim for at least 20-30 minutes of exercise per day, but be sure to consult with your veterinarian to determine the appropriate amount of exercise for your cat’s individual needs.
Walking on a Leash
Some cats enjoy walking on a leash, which can provide exercise and mental stimulation. However, not all cats are comfortable with this, so be sure to introduce the leash slowly and with positive reinforcement. Always supervise your cat when walking on a leash and be sure to use a properly fitting harness.
By incorporating regular exercise and playtime into your cat’s routine, you can help manage their diabetes and improve their overall health and well-being. Work with your veterinarian to develop an exercise plan that meets your cat’s individual needs.

Working with Your Vet: Collaborating for Your Cat’s Health
Collaborating with your veterinarian is essential for managing feline diabetes. Your vet can provide you with valuable guidance and support throughout your cat’s diabetes management journey. This section will cover some tips for working with your vet to ensure your cat’s health.
Regular Check-Ups
Regular check-ups with your veterinarian are important for cats with diabetes. Your vet can monitor your cat’s blood sugar levels, assess their overall health, and identify any potential complications early on. Be sure to follow your vet’s recommended schedule for check-ups and communicate any concerns or changes in your cat’s behavior or health.
Open Communication
Open communication with your veterinarian is key to ensuring your cat’s health. Be sure to ask questions, share concerns, and provide updates on your cat’s diabetes management. Your vet can offer advice and guidance to help you manage your cat’s diabetes effectively.
Follow Treatment Plans
Following your veterinarian’s treatment plan is crucial for managing feline diabetes. This may include regular blood glucose monitoring, insulin therapy, prescription diets, exercise, and lifestyle changes. Be sure to follow your vet’s instructions carefully and report any issues or concerns as soon as possible.
Be Prepared for Emergencies
It’s important to be prepared for emergencies related to your cat’s diabetes. This may include having an emergency kit on hand with insulin, syringes, and other necessary supplies, as well as knowing the signs of hypoglycemia and what to do in case of an emergency. Your veterinarian can provide you with guidance on how to handle emergencies related to feline diabetes.
Collaborate with a Specialist
In some cases, your veterinarian may refer you to a specialist, such as a veterinary endocrinologist, for additional support and expertise. Collaborating with a specialist can provide you with additional resources and support to manage your cat’s diabetes effectively.
By working closely with your veterinarian and following their recommended treatment plan, you can help manage your cat’s diabetes and ensure their long-term health and well-being. Don’t hesitate to reach out to your veterinarian for support and guidance throughout your cat’s diabetes management journey.
Living with a Diabetic Cat: Coping Strategies and Emotional Support.
Living with a diabetic cat can be a challenging and emotional experience. It’s important to take care of yourself and seek out support as needed. This section will cover some coping strategies and emotional support for living with a diabetic cat.
Educate Yourself
Educating yourself about feline diabetes can help you better understand your cat’s condition and feel more confident in managing it. Talk to your veterinarian, read books and articles, and join online support groups to learn more about feline diabetes and how to manage it effectively.
Practice Self-Care
Taking care of yourself is important when living with a diabetic cat. This can include practicing self-care activities such as exercise, meditation, and spending time with friends and family. Make sure to prioritize your own health and well-being, so that you can better care for your cat.
Connect with Others
Connecting with others who have experience caring for a diabetic cat can provide valuable emotional support and practical advice. Consider joining online support groups or attending local meetups for cat owners. Talking to others who understand what you’re going through can help you feel less alone and more supported.
Seek Professional Support
If you’re feeling overwhelmed or struggling to cope with the demands of caring for a diabetic cat, consider seeking professional support. This may include talking to a therapist, counselor, or support group. A mental health professional can help you develop coping strategies and provide emotional support.
Celebrate Small Wins
Caring for a diabetic cat can be a long and challenging journey, but it’s important to celebrate small wins along the way. Whether it’s a successful blood sugar reading or a fun playtime session, taking time to appreciate the positive moments can help boost your mood and motivation.
By practicing self-care, connecting with others, seeking professional support, and celebrating small wins, you can better cope with the demands of caring for a diabetic cat. Remember to prioritize your own health and well-being, so that you can provide the best possible care for your beloved pet.