Table of Contents
- Understanding Feline Glaucoma: Overview and Causes
- Recognizing Symptoms of Feline Glaucoma in Cats
- Types of Glaucoma in Cats: Primary vs. Secondary
- Diagnosing Feline Glaucoma: What to Expect
- Treatment Options for Feline Glaucoma: Medications and Surgery
- Managing Glaucoma in Cats: Lifestyle Changes and Home Care
- Potential Complications and Prognosis for Feline Glaucoma
- Preventing Feline Glaucoma: Tips and Best Practices for Cat Owners
Understanding Feline Glaucoma: Overview and Causes
Feline glaucoma is a serious eye condition that can cause blindness if not treated promptly. It occurs when there is increased pressure within the eye, which damages the optic nerve and impairs vision. In this section, we’ll delve deeper into what glaucoma is, how it affects cats, and what the potential causes of this condition are.
How Glaucoma Affects the Eyes
To understand how glaucoma affects the eyes, it’s important to know a little bit about the anatomy of the eye. The eye is filled with a clear fluid called aqueous humor, which helps to nourish the tissues inside the eye. Normally, this fluid flows in and out of the eye at a steady rate, but in cats with glaucoma, the fluid can’t drain properly, causing pressure to build up within the eye. This pressure damages the optic nerve, leading to vision loss and eventual blindness.
Primary vs. Secondary Glaucoma
There are two main types of Glaucoma in cats: primary and secondary. Primary glaucoma occurs when there is a problem with the drainage system inside the eye, which can be due to a genetic predisposition. Secondary glaucoma, on the other hand, is usually caused by an underlying condition, such as uveitis (inflammation of the eye), a tumor, or trauma to the eye.
Causes of Feline Glaucoma
The causes of feline glaucoma are not fully understood, but it’s believed that genetics may play a role in primary glaucoma. Some cat breeds are more predisposed to developing glaucoma, including Siamese, Persian, and Burmese cats. In secondary glaucoma, the underlying cause can vary, but it’s usually related to an injury or inflammation in the eye.
It’s important to note that glaucoma can occur in cats of all ages, although it’s more common in older cats. Additionally, cats with certain medical conditions, such as diabetes or high blood pressure, may be more at risk for developing glaucoma.
In the next section, we’ll discuss how to recognize the symptoms of feline glaucoma, so that you can seek treatment for your cat as soon as possible.

Recognizing Symptoms of Feline Glaucoma in Cats
Because feline glaucoma can cause irreversible blindness if left untreated, it’s important to be able to recognize the symptoms of this condition as soon as possible. Here are some signs that your cat may be experiencing glaucoma:
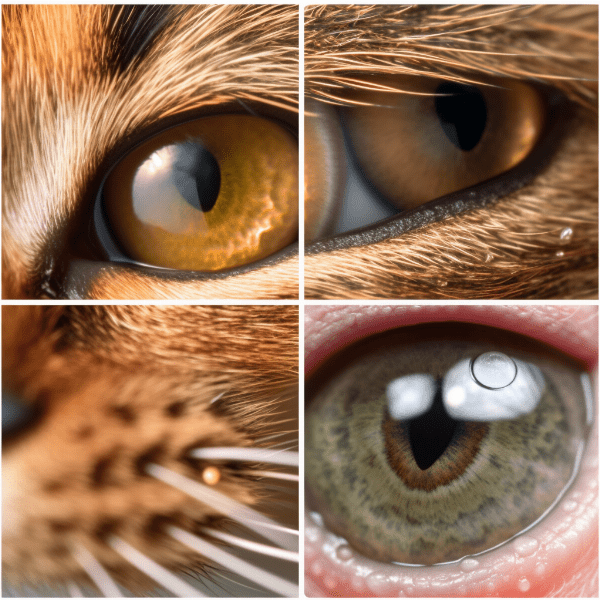
Cloudy or Red Eyes
One of the most common signs of glaucoma in cats is cloudy or red eyes. This is because the increased pressure within the eye can cause blood vessels to burst and irritate the eye, leading to redness and cloudiness.
Dilated Pupil
Another sign of glaucoma in cats is a dilated pupil. This is because the pressure within the eye can cause the pupil to enlarge, making it difficult for the eye to adjust to changes in light.
Squinting or Blinking
Cats with glaucoma may also squint or blink frequently, as the increased pressure in the eye can cause discomfort and sensitivity to light.
Vision Loss
As glaucoma progresses, cats may begin to experience vision loss. This can manifest as bumping into objects or appearing disoriented.
Behavioral Changes
Cats with glaucoma may also exhibit behavioral changes, such as becoming more lethargic or irritable. This is because the discomfort and pain associated with glaucoma can cause cats to become less active and more withdrawn.
If you notice any of these symptoms in your cat, it’s important to seek veterinary care as soon as possible. In the next section, we’ll discuss the different types of glaucoma in cats and how they are diagnosed.

Types of Glaucoma in Cats: Primary vs. Secondary
There are two main types of glaucoma in cats: primary and secondary. Understanding the differences between these types of glaucoma is important for diagnosis and treatment.
Primary Glaucoma
Primary glaucoma is caused by an inherited abnormality in the drainage system within the eye. It is more common in certain breeds of cats, including Siamese, Persian, and Burmese. Primary glaucoma is typically bilateral, meaning it affects both eyes, although it may not be present in both eyes at the same time. This type of glaucoma is more difficult to treat and can progress more rapidly than secondary glaucoma.
Secondary Glaucoma
Secondary glaucoma is caused by an underlying condition or disease, such as uveitis, trauma to the eye, or a tumor. It can affect one or both eyes and may develop more quickly than primary glaucoma. Secondary glaucoma can also occur as a complication of certain medications or treatments, such as corticosteroids.
Development of Glaucoma
Regardless of the type of glaucoma, the development of this condition is gradual and may not be noticed until the disease has progressed significantly. This is why routine veterinary check-ups are so important, particularly as your cat ages.
In the next section, we’ll discuss how feline glaucoma is diagnosed, and what you can expect during a veterinary examination.
Diagnosing Feline Glaucoma: What to Expect
If you suspect that your cat may have glaucoma, it’s important to schedule an appointment with your veterinarian as soon as possible. Here’s what you can expect during a veterinary examination for feline glaucoma:
Eye Exam
The first step in diagnosing feline glaucoma is a thorough eye exam. Your veterinarian will examine your cat’s eyes for any signs of cloudiness, redness, or other abnormalities. They may also measure the pressure within the eye using a tonometer.
Imaging Tests
In some cases, your veterinarian may recommend additional imaging tests to help diagnose glaucoma. This may include ultrasound, which can help visualize the structures within the eye, or radiographs to rule out any underlying conditions.
Referral to a Veterinary Ophthalmologist
If your veterinarian suspects that your cat has glaucoma, they may refer you to a veterinary ophthalmologist for further testing and treatment. An ophthalmologist is a veterinarian who specializes in diagnosing and treating eye conditions in animals.
Monitoring Progression
If your cat is diagnosed with glaucoma, it’s important to monitor the progression of the disease over time. Your veterinarian may recommend regular check-ups to assess the pressure within the eye and monitor any changes in your cat’s vision.
Early detection and treatment of feline glaucoma is crucial for preserving your cat’s vision. In the next section, we’ll discuss the different treatment options for feline glaucoma, including medications and surgery.
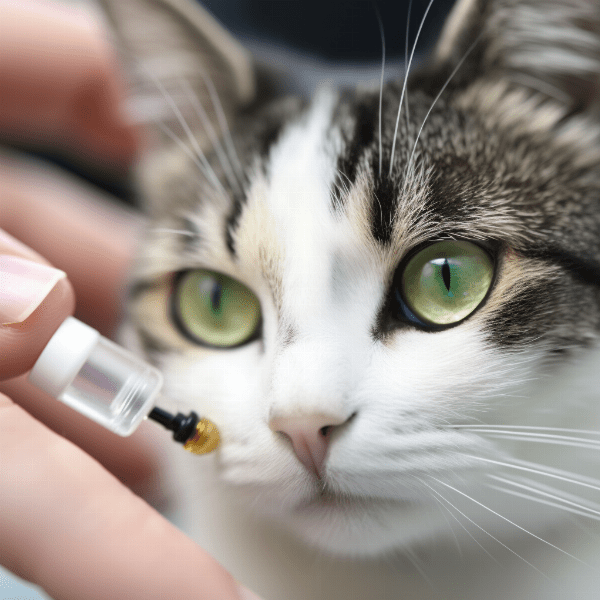
Treatment Options for Feline Glaucoma: Medications and Surgery
There are several treatment options available for feline glaucoma, including medications and surgery. The goal of treatment is to lower the pressure within the eye and preserve your cat’s vision.
Medications
In many cases, feline glaucoma can be managed with medication. Your veterinarian may prescribe eye drops or oral medications to help reduce the pressure within the eye. These medications work by either decreasing the production of aqueous humor or increasing the outflow of fluid from the eye.
Surgery
In some cases, surgery may be necessary to treat feline glaucoma. There are several surgical options available, including laser therapy, cyclophotocoagulation, and filtration surgery. These procedures aim to increase the outflow of fluid from the eye and reduce the pressure within the eye.
Combination Therapy
In some cases, a combination of medication and surgery may be necessary to effectively manage feline glaucoma. Your veterinarian will work with you to determine the best treatment plan for your cat based on the type and severity of the glaucoma.
Managing Pain
It’s important to note that feline glaucoma can be painful for your cat, particularly as the disease progresses. Your veterinarian may prescribe pain medication or recommend other pain management strategies to help keep your cat comfortable.
Follow-Up Care
If your cat undergoes surgery for glaucoma, it’s important to follow up with your veterinarian for regular check-ups to monitor the success of the procedure and ensure that the pressure within the eye remains under control.
In the next section, we’ll discuss some lifestyle changes and home care strategies that can help manage feline glaucoma.
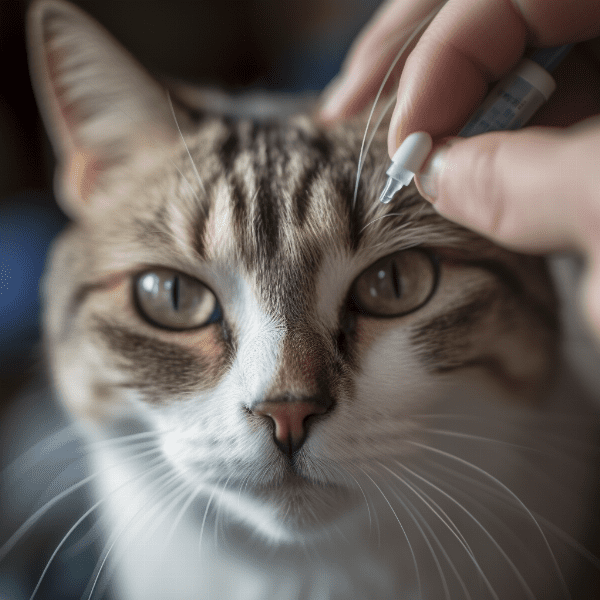

Managing Glaucoma in Cats: Lifestyle Changes and Home Care
In addition to medications and surgery, there are several lifestyle changes and home care strategies that can help manage feline glaucoma and improve your cat’s quality of life.
Reducing Stress
Stress can exacerbate the symptoms of glaucoma, so it’s important to minimize stress in your cat’s environment as much as possible. This may include providing a quiet and comfortable space for your cat to rest, minimizing exposure to loud noises or other stressors, and providing plenty of mental and physical stimulation.
Managing Diet
Your cat’s diet can also play a role in managing glaucoma. Some studies suggest that a diet high in antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids may help reduce inflammation and protect the eye from damage. Talk to your veterinarian about whether a dietary change may be appropriate for your cat.
Environmental Adaptations
As your cat’s vision deteriorates, you may need to make some adaptations to your home environment to help your cat navigate and avoid injury. This may include placing ramps or stairs near furniture, using tactile markers to help your cat find their way around, and keeping hazardous objects out of your cat’s path.
Regular Check-Ups
Regular check-ups with your veterinarian are important for monitoring the progression of glaucoma and adjusting treatment as necessary. Your veterinarian may recommend more frequent check-ups if your cat’s glaucoma is severe or if they have undergone surgery for the condition.
Eye Care
In addition to medications and surgery, your cat’s eye care is also important for managing glaucoma. This may include regular cleaning of the eyes, administration of eye drops or ointments, and monitoring for any signs of infection or other complications.
By making some lifestyle changes and providing appropriate home care, you can help manage your cat’s glaucoma and improve their quality of life. In the next section, we’ll discuss the potential complications and prognosis for feline glaucoma.

Potential Complications and Prognosis for Feline Glaucoma
Feline glaucoma is a serious condition that can lead to blindness if not treated promptly and effectively. In this section, we’ll discuss some potential complications of feline glaucoma, as well as the prognosis for cats with this condition.
Complications
If left untreated, feline glaucoma can cause irreversible damage to the optic nerve and lead to blindness. In addition, the increased pressure within the eye can cause discomfort and pain for your cat, which can impact their quality of life.
Prognosis
The prognosis for feline glaucoma depends on several factors, including the severity of the condition, the type of glaucoma, and the age and overall health of the cat. While glaucoma cannot be cured, early detection and treatment can help slow the progression of the disease and preserve your cat’s vision. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to effectively manage the condition.
It’s important to note that even with treatment, some cats with glaucoma may still experience vision loss or blindness. However, with appropriate care and management, cats with glaucoma can still lead happy and fulfilling lives.
In the next section, we’ll discuss some tips and best practices for preventing feline glaucoma and maintaining your cat’s overall eye health.

Preventing Feline Glaucoma: Tips and Best Practices for Cat Owners
While feline glaucoma cannot always be prevented, there are several tips and best practices that cat owners can follow to help reduce their cat’s risk of developing this condition.
Regular Eye Exams
Regular eye exams with your veterinarian are important for monitoring your cat’s eye health and detecting any potential problems early on. This is especially important for older cats, as they are more at risk for developing glaucoma.
Health Monitoring
Monitoring your cat’s overall health can also help prevent feline glaucoma. Regular check-ups with your veterinarian can help detect underlying medical conditions, such as high blood pressure or diabetes, which can increase the risk of glaucoma.
Genetics
If you are considering adopting a cat or adding a new cat to your household, it’s important to research the breed’s predisposition to glaucoma. Some cat breeds, such as Siamese, Persian, and Burmese, are more at risk for developing glaucoma than others.
Environmental Modifications
Making some simple environmental modifications can also help prevent feline glaucoma. This may include keeping hazardous objects out of your cat’s path, using a soft bed or cushion to reduce pressure on the eyes while resting, and providing plenty of mental and physical stimulation to reduce stress.
Nutrition
Providing your cat with a well-balanced and nutritious diet can also help promote overall eye health. Talk to your veterinarian about whether a diet high in antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids may be beneficial for your cat.
By following these tips and best practices, you can help reduce your cat’s risk of developing feline glaucoma and promote their overall eye health. If you suspect that your cat may be experiencing glaucoma, it’s important to seek veterinary care as soon as possible.




